contingency
contingency.Rmd
library(MinervaTime)Model a simple contingency scenario. When A is presented for 20 time steps as the first event, C is followed at time point 50. When B is presented 20 time steps as the first event, D is followed at time point 50. E is the ever-present context. 5 trials of intermixed training.
trial_timesteps = 200
timeline <- rbind(make_trial(1,c("A","C","E"),c(1,50,1),c(20,20,199)),
make_trial(2,c("B","D","E"),c(1,50,1),c(20,20,199)),
make_trial(3,c("A","C","E"),c(1,50,1),c(20,20,199)),
make_trial(4,c("B","D","E"),c(1,50,1),c(20,20,199)),
make_trial(5,c("A","C","E"),c(1,50,1),c(20,20,199)),
make_trial(6,c("B","D","E"),c(1,50,1),c(20,20,199)),
make_trial(7,c("A","C","E"),c(1,50,1),c(20,20,199)),
make_trial(8,c("B","D","E"),c(1,50,1),c(20,20,199)),
make_trial(9,c("A","C","E"),c(1,50,1),c(20,20,199)),
make_trial(10,c("B","D","E"),c(1,50,1),c(20,20,199))
)
# convert timeline to environment vectors
temporal_vectors <- make_temporal_vectors(trial_timesteps, overlap = 2)
event_vectors <- make_event_vectors(LETTERS[1:10],10)
timeline_vectors <- timeline_to_vector(timeline,
event_vectors,
temporal_vectors,200)Run model
## define basic model parameters
library(RsemanticLibrarian) # for cosine_x_to_m
# initialize memory with 5 noise vectors
environment_matrix <- timeline_vectors[[1]]
noise <- matrix(runif(5*dim(environment_matrix)[2],-1,1)*.05,
nrow = 5,
ncol = dim(environment_matrix)[2])
memory <- noise
tau <- 3
## Run the model for each trial
model_results <- list()
for(t in 1:length(timeline_vectors)) {
environment_matrix <- timeline_vectors[[t]]
save_echo <- matrix(0,
nrow=dim(environment_matrix)[1],
ncol=dim(environment_matrix)[2])
# intra-trial encoding and retrieval
for (i in 1:dim(environment_matrix)[1]){
activations <- c(cosine_x_to_m(environment_matrix[i,],
memory)^tau)
echo <- colSums(memory*activations)
save_echo[i,] <- echo
memory <- rbind(memory,environment_matrix[i,])
}
A_expectation <- rowMeans(save_echo[,1:10])
B_expectation <- rowMeans(save_echo[,11:20])
C_expectation <- rowMeans(save_echo[,21:30])
D_expectation <- rowMeans(save_echo[,31:40])
model_results[[t]] <- list(A_expectation = A_expectation,
B_expectation = B_expectation,
C_expectation = C_expectation,
D_expectation = D_expectation,
save_echo = save_echo)
}plot model results
Shows the model’s expectation for the B event across a trial window, after the 1st, 5th, and 10th trial.
# trial 9 was A <-> C
# trial 10 was B <->D
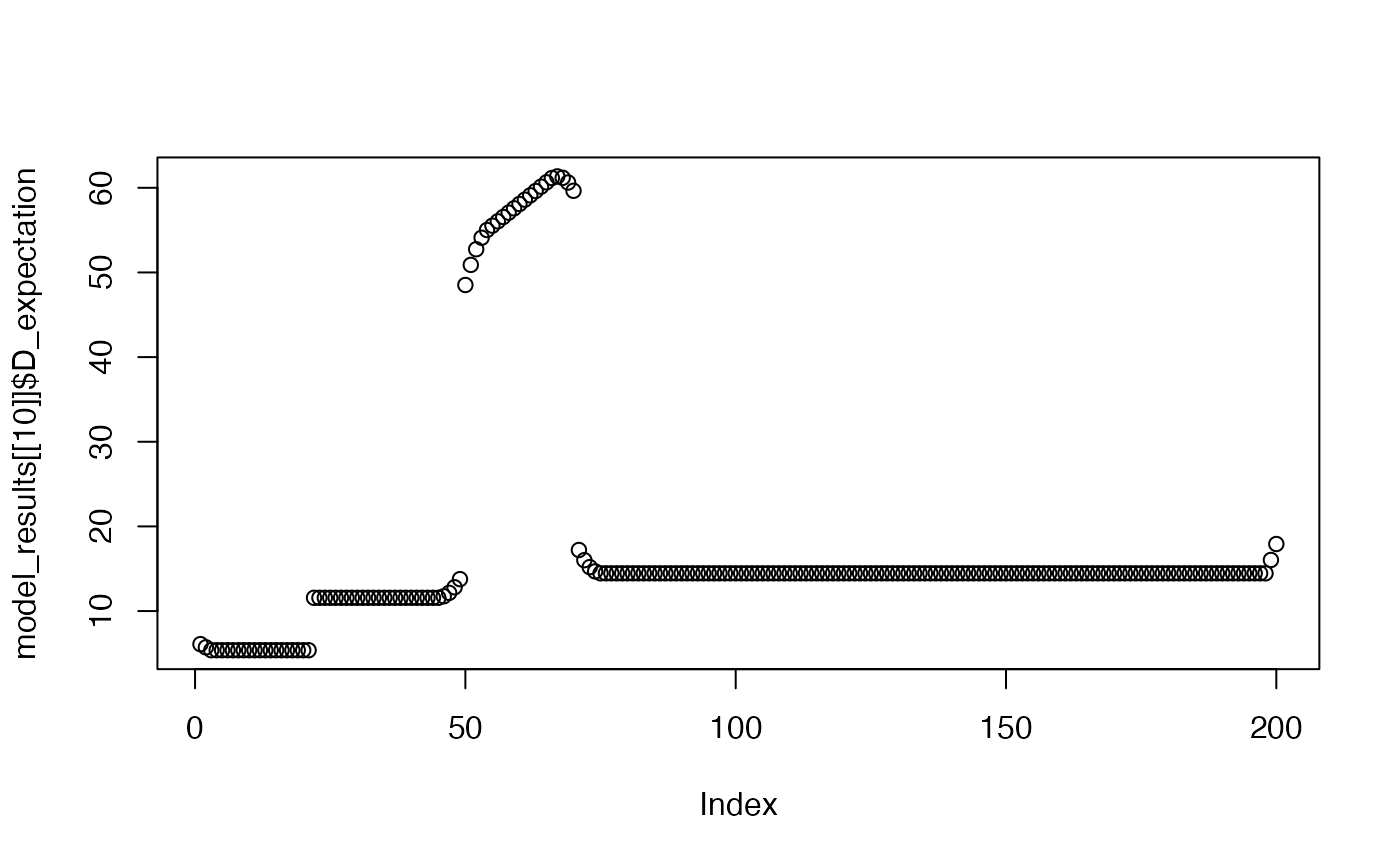
plot(model_results[[1]]$A_expectation)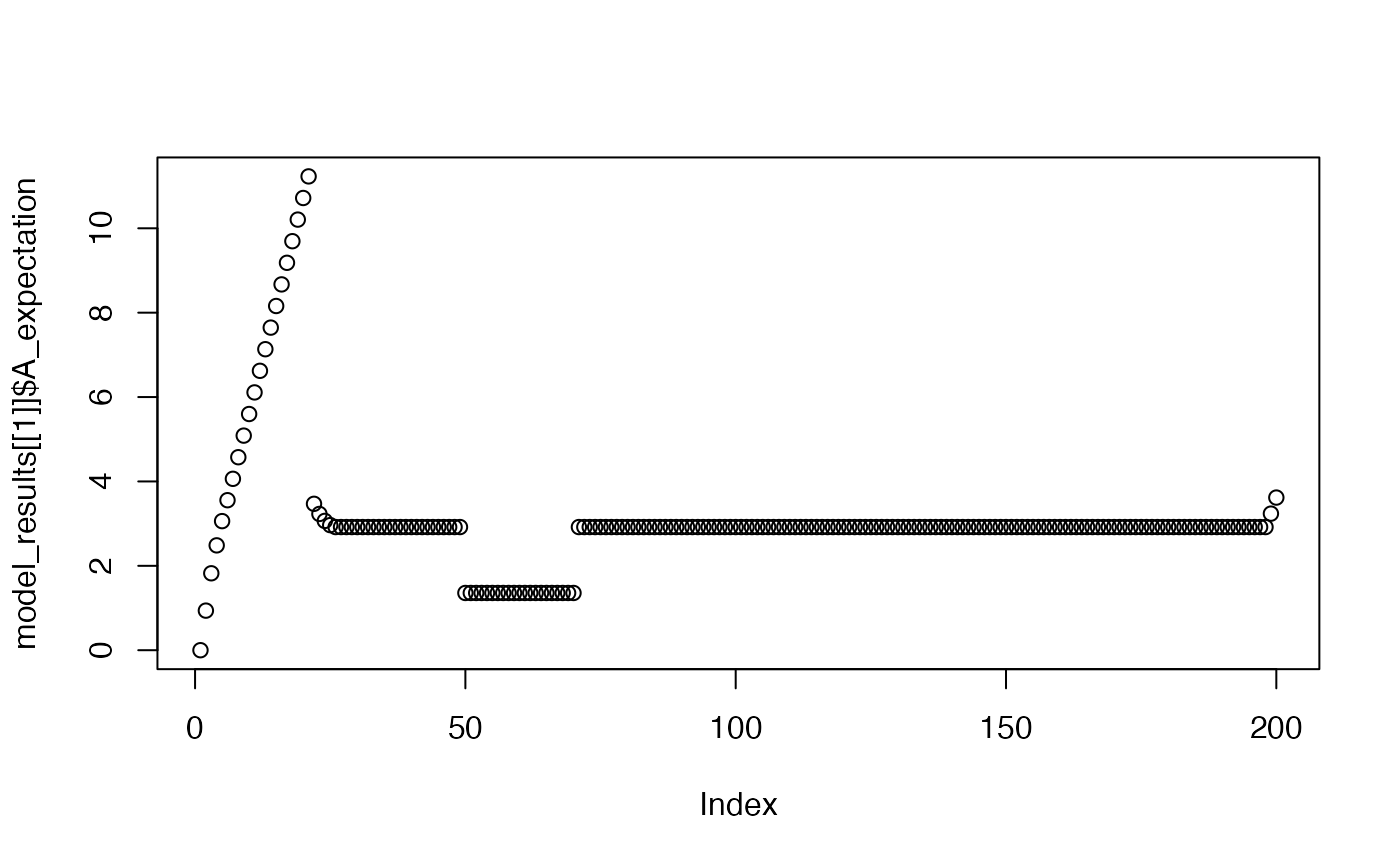
plot(model_results[[1]]$B_expectation)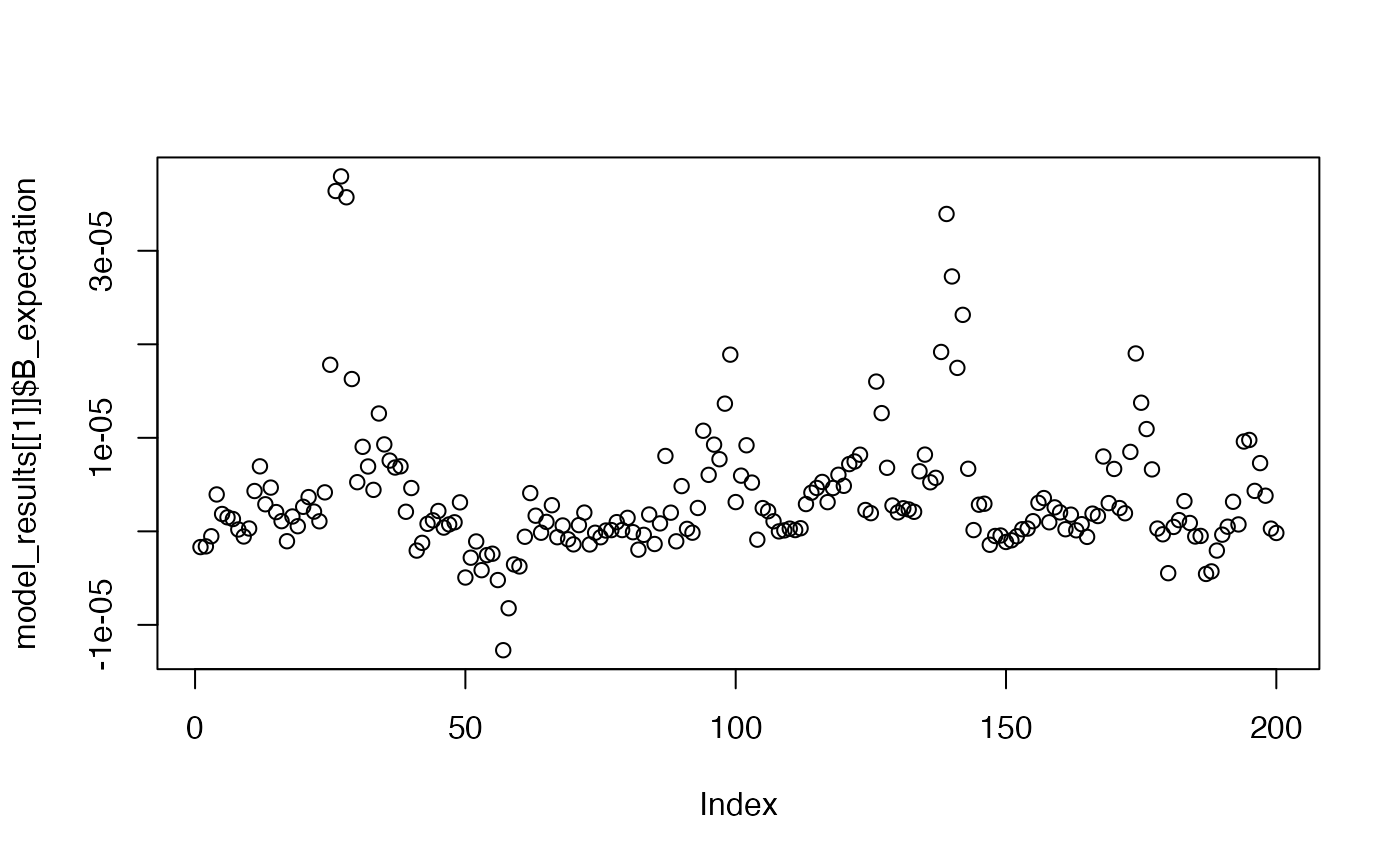
plot(model_results[[1]]$C_expectation)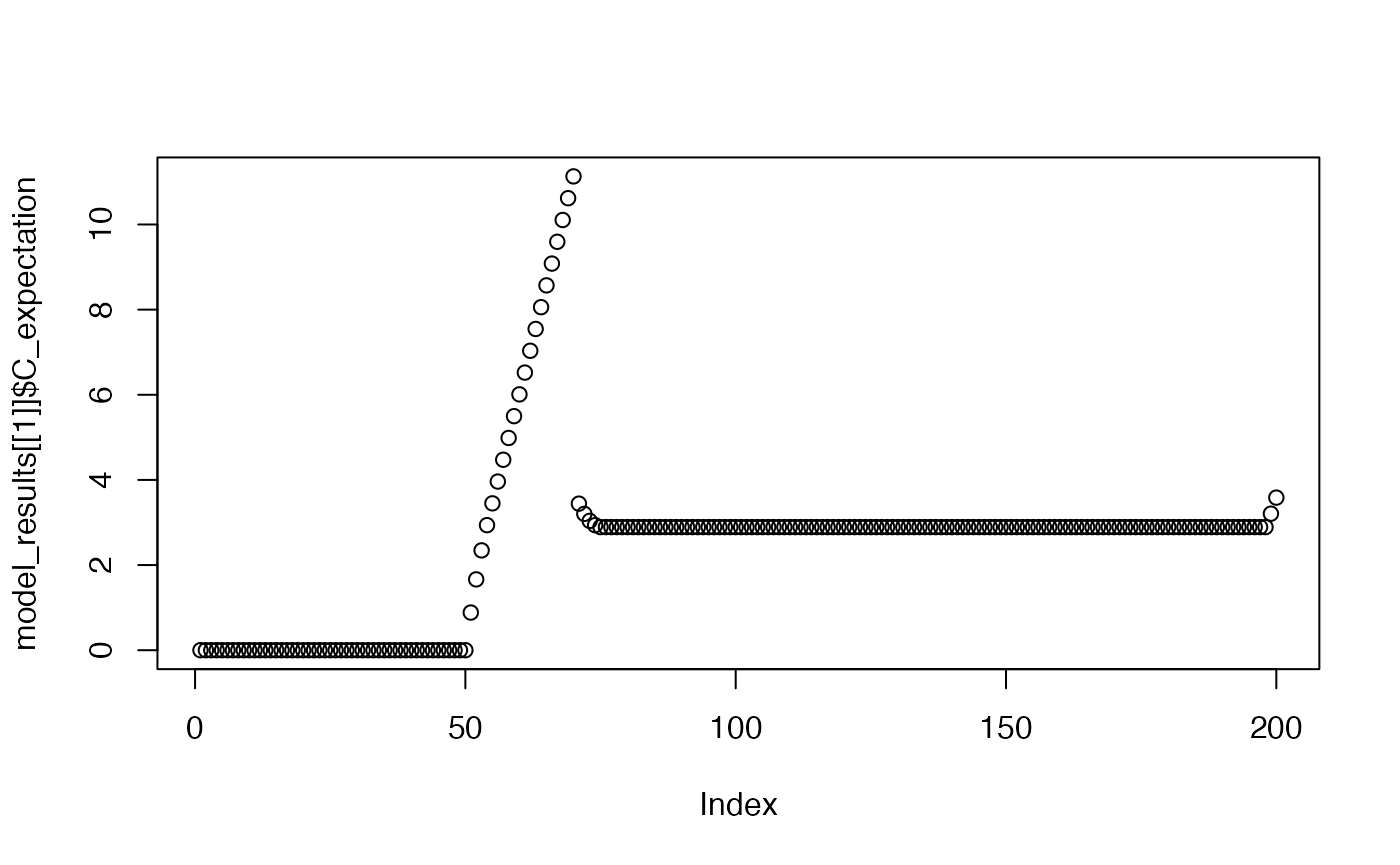
plot(model_results[[1]]$D_expectation)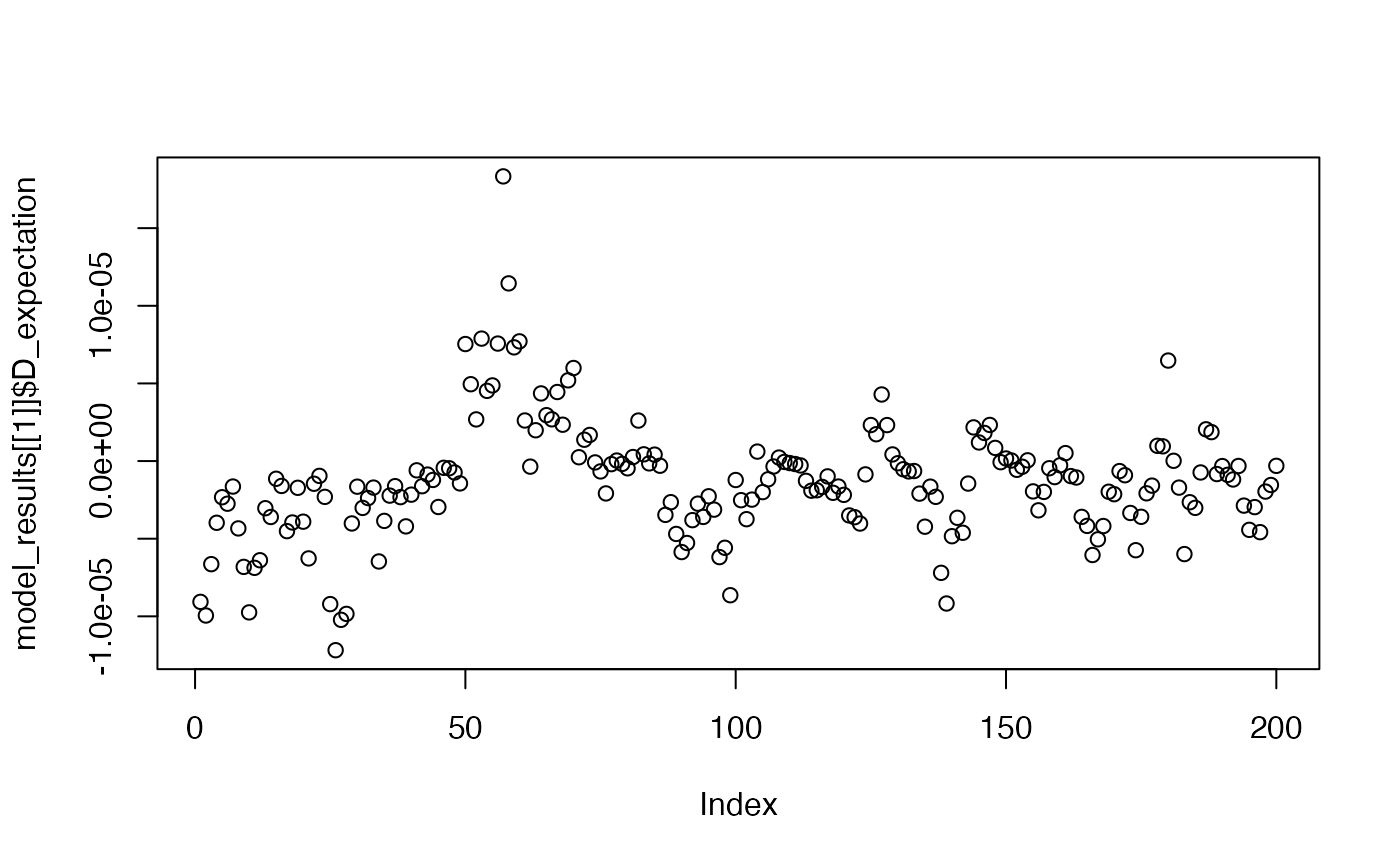
plot(model_results[[2]]$A_expectation)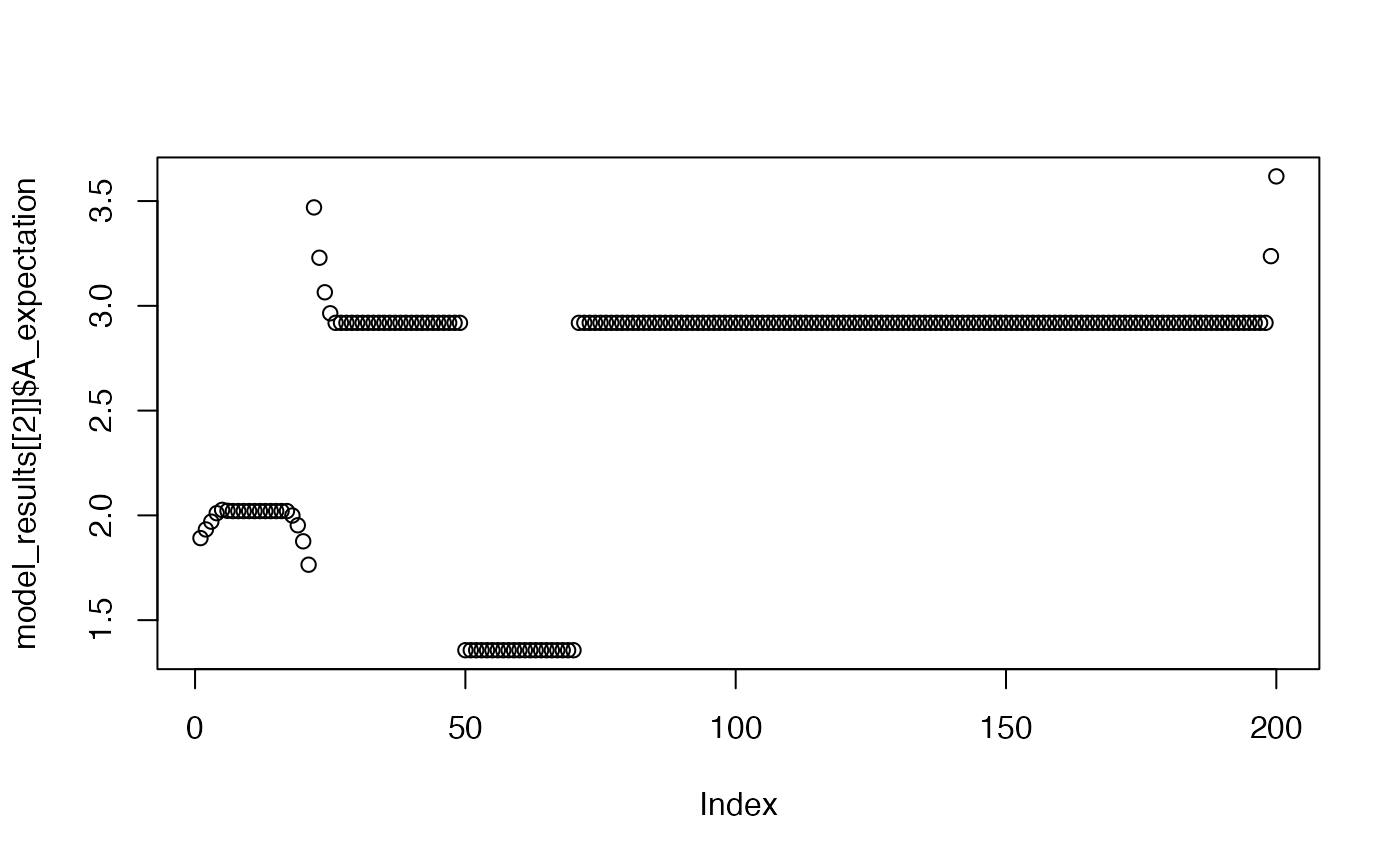
plot(model_results[[2]]$B_expectation)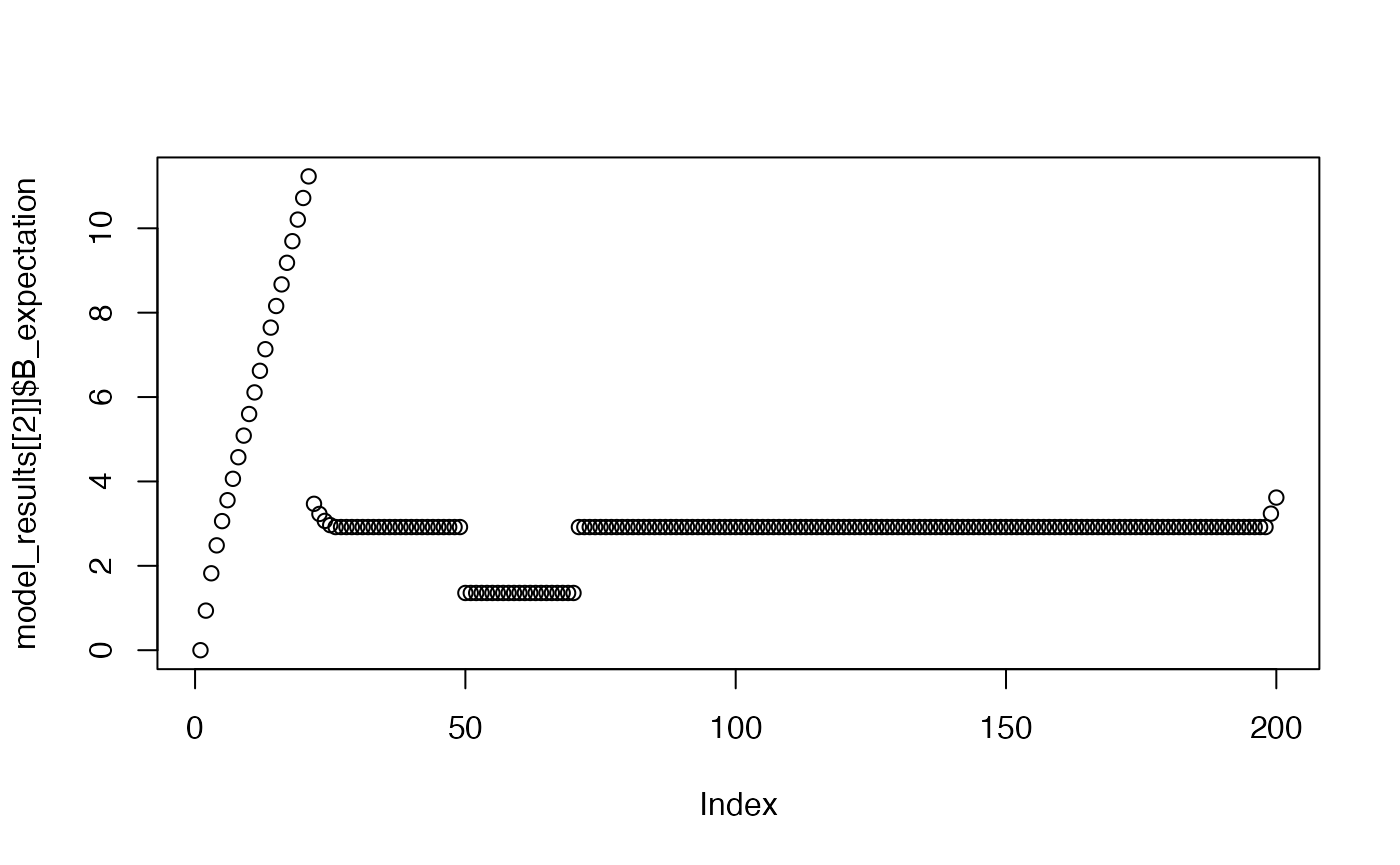
plot(model_results[[2]]$C_expectation)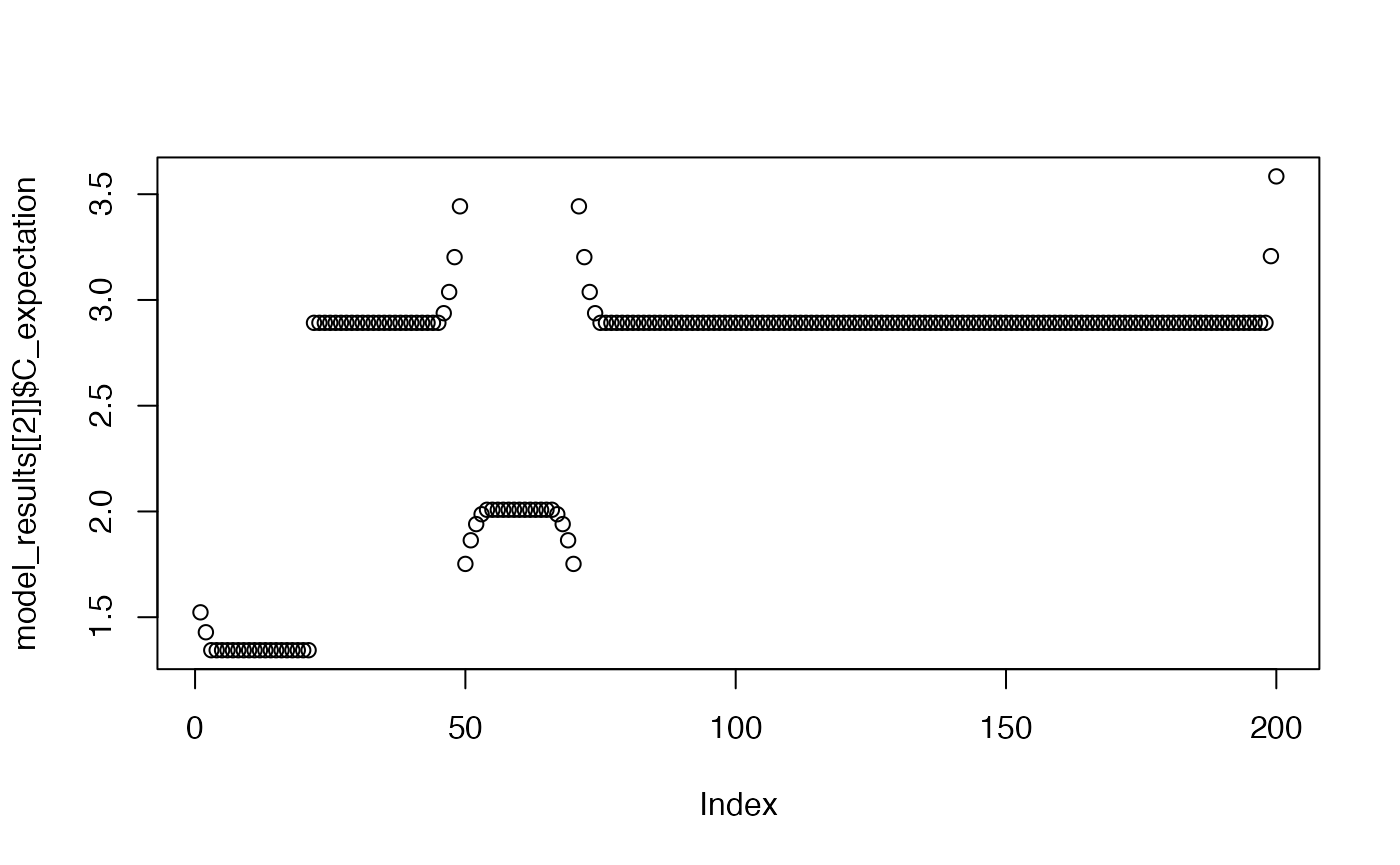
plot(model_results[[2]]$D_expectation)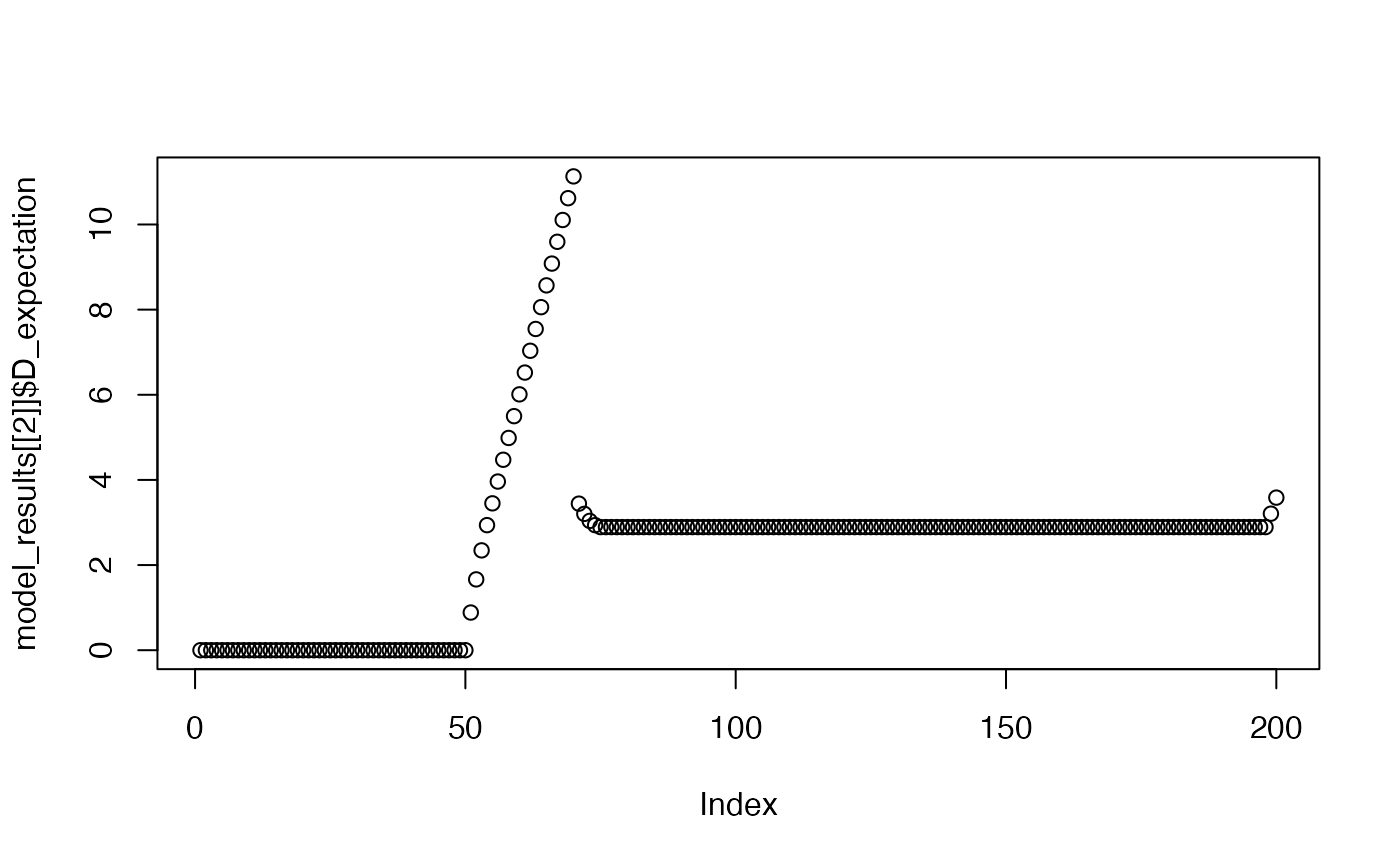
plot(model_results[[3]]$A_expectation)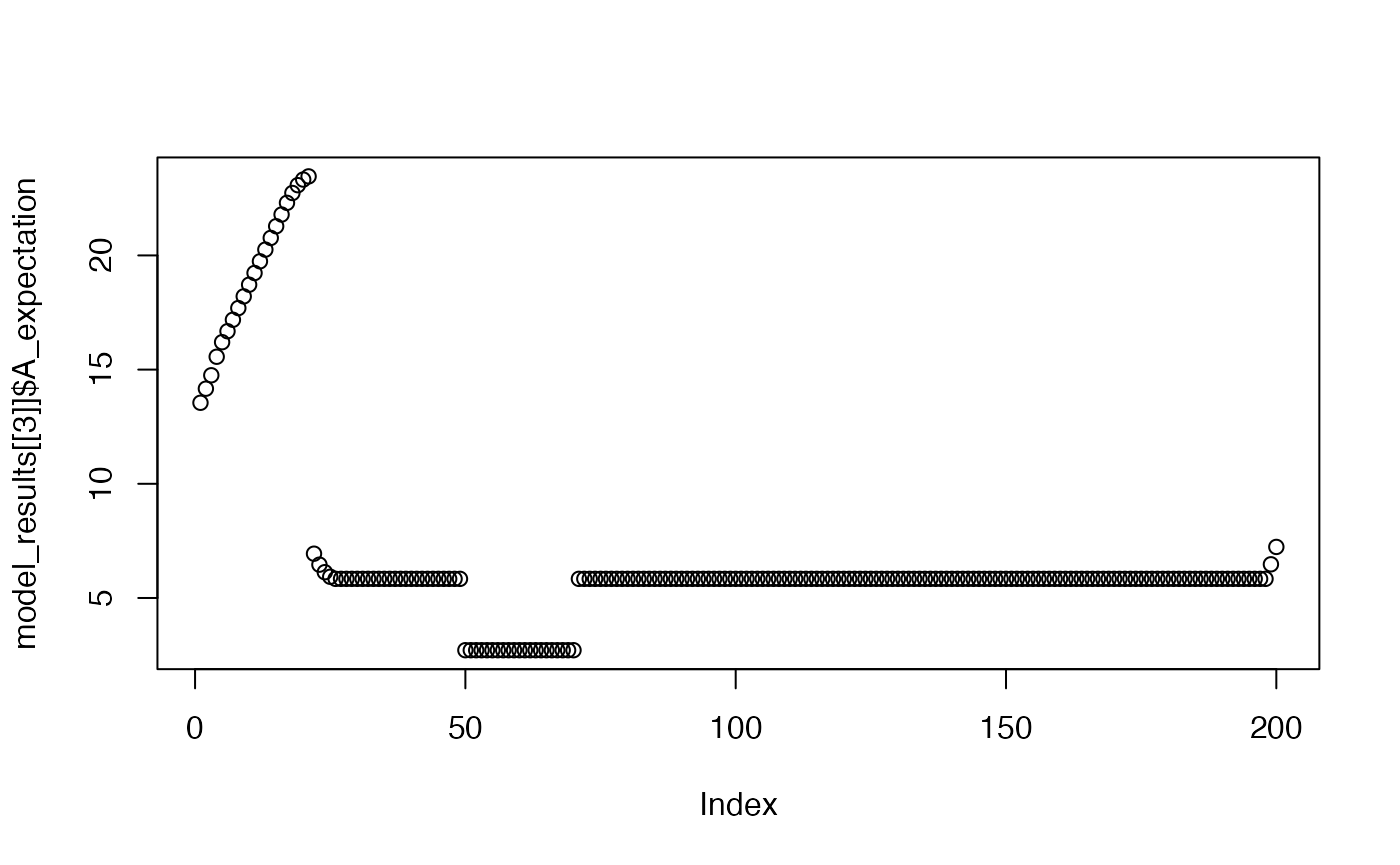
plot(model_results[[3]]$B_expectation)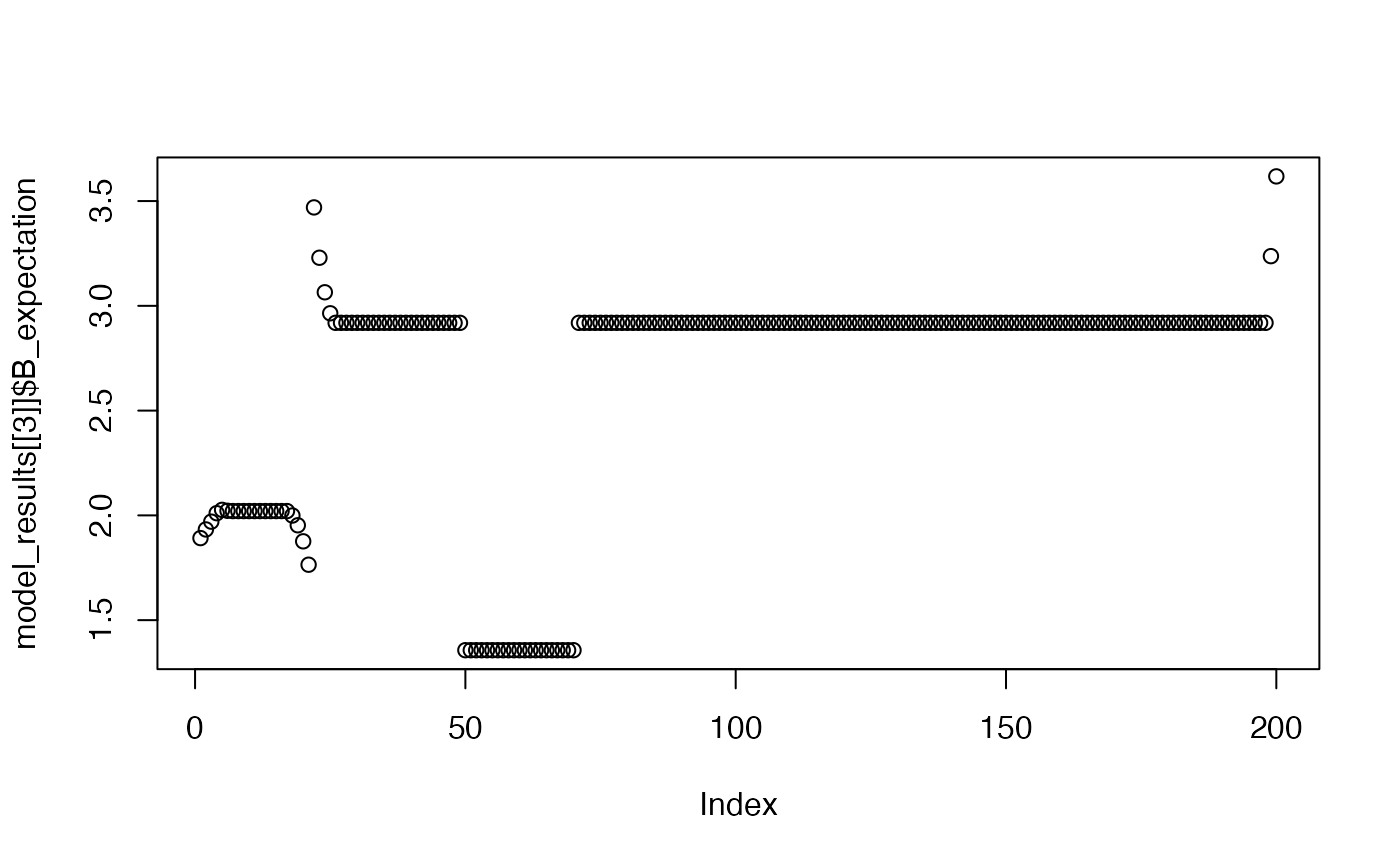
plot(model_results[[3]]$C_expectation)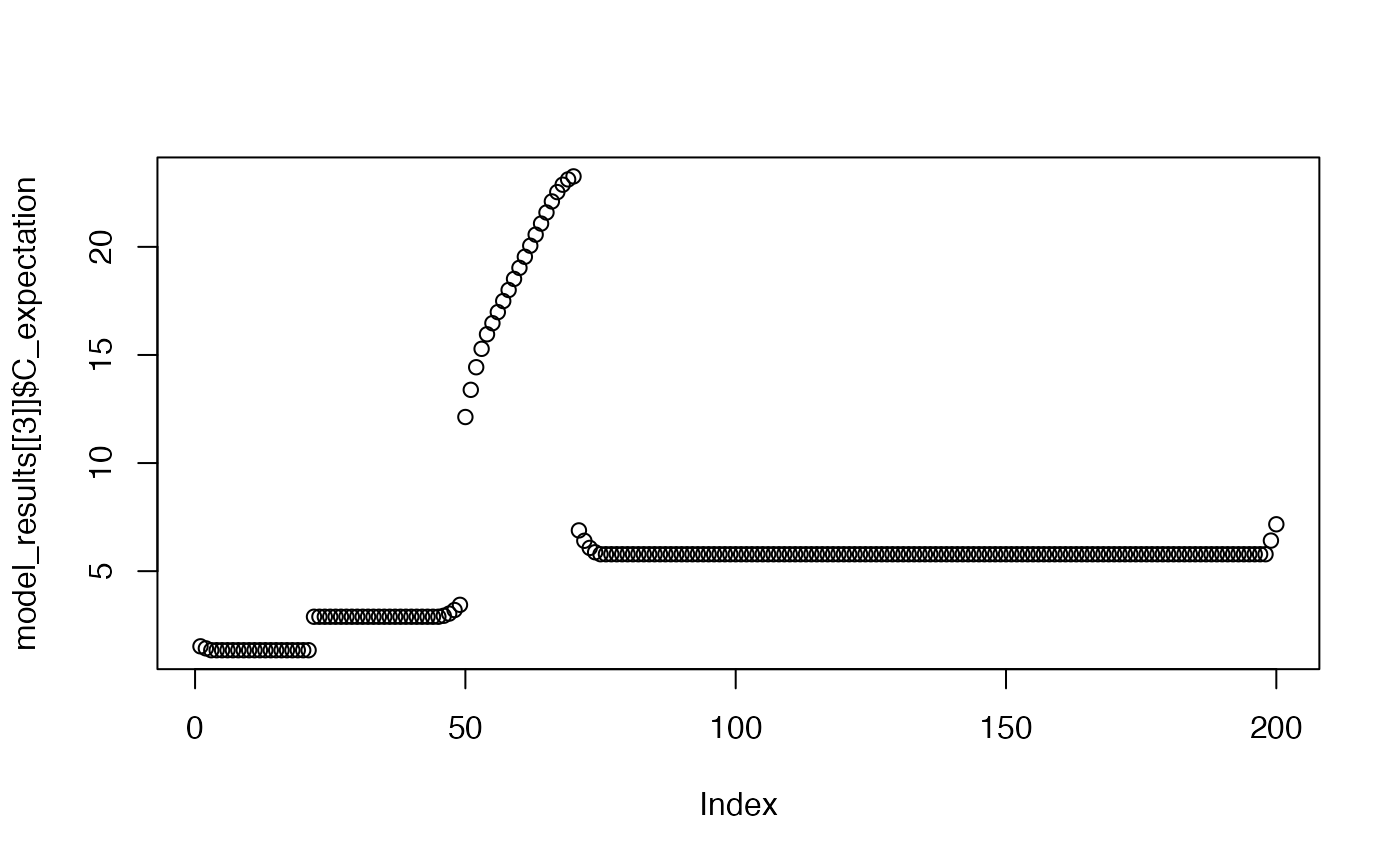
plot(model_results[[3]]$D_expectation)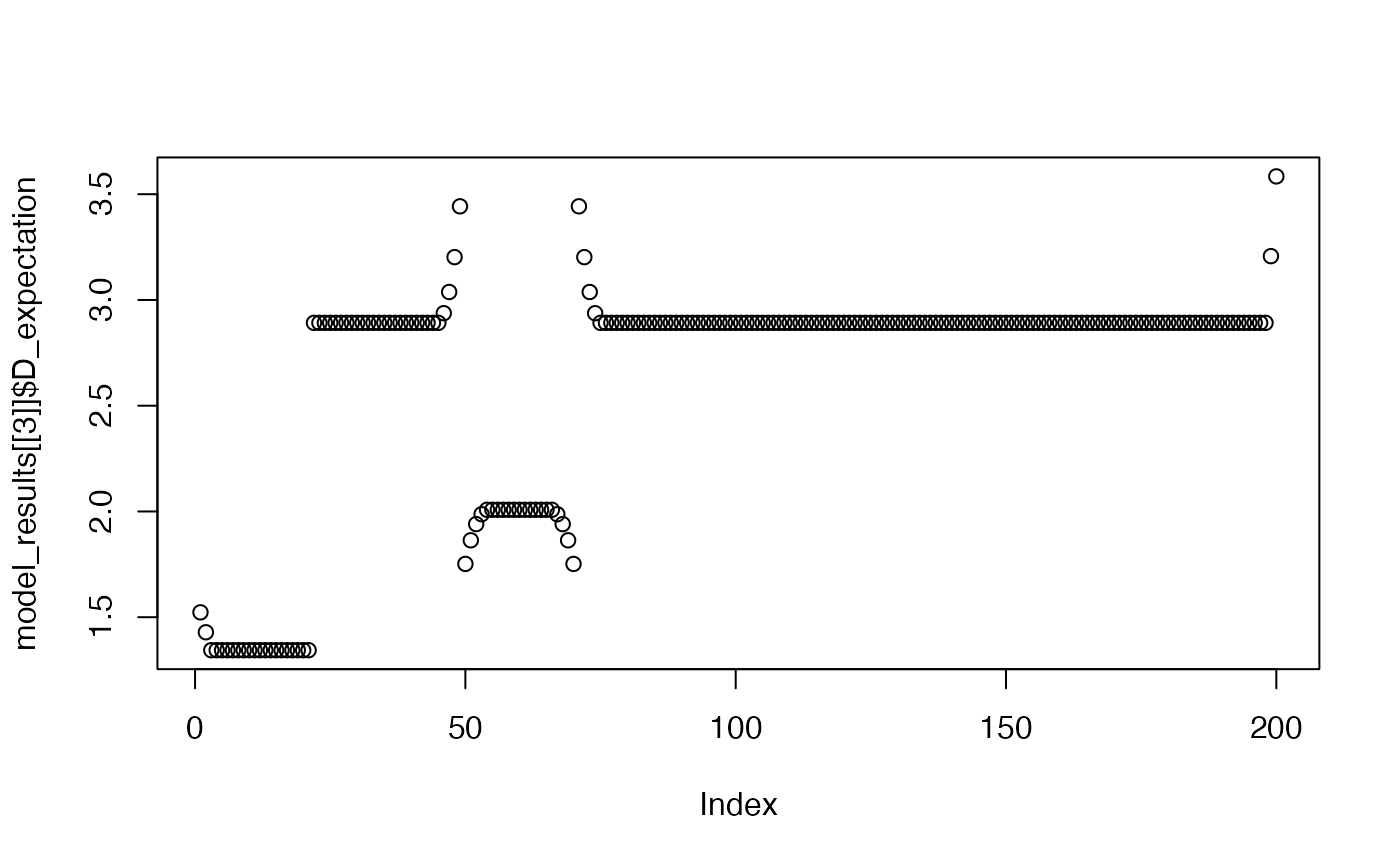
plot(model_results[[4]]$A_expectation)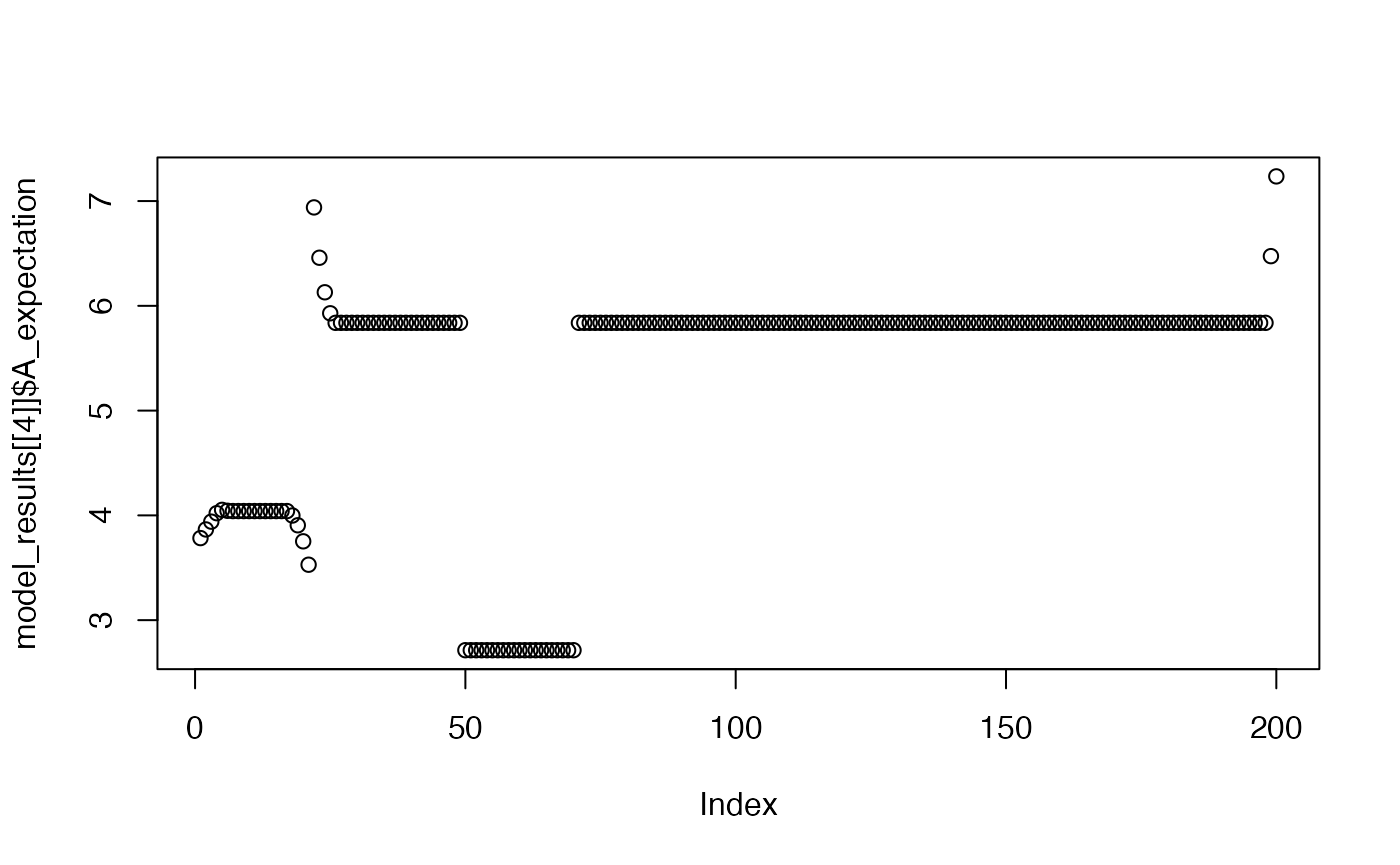
plot(model_results[[4]]$B_expectation)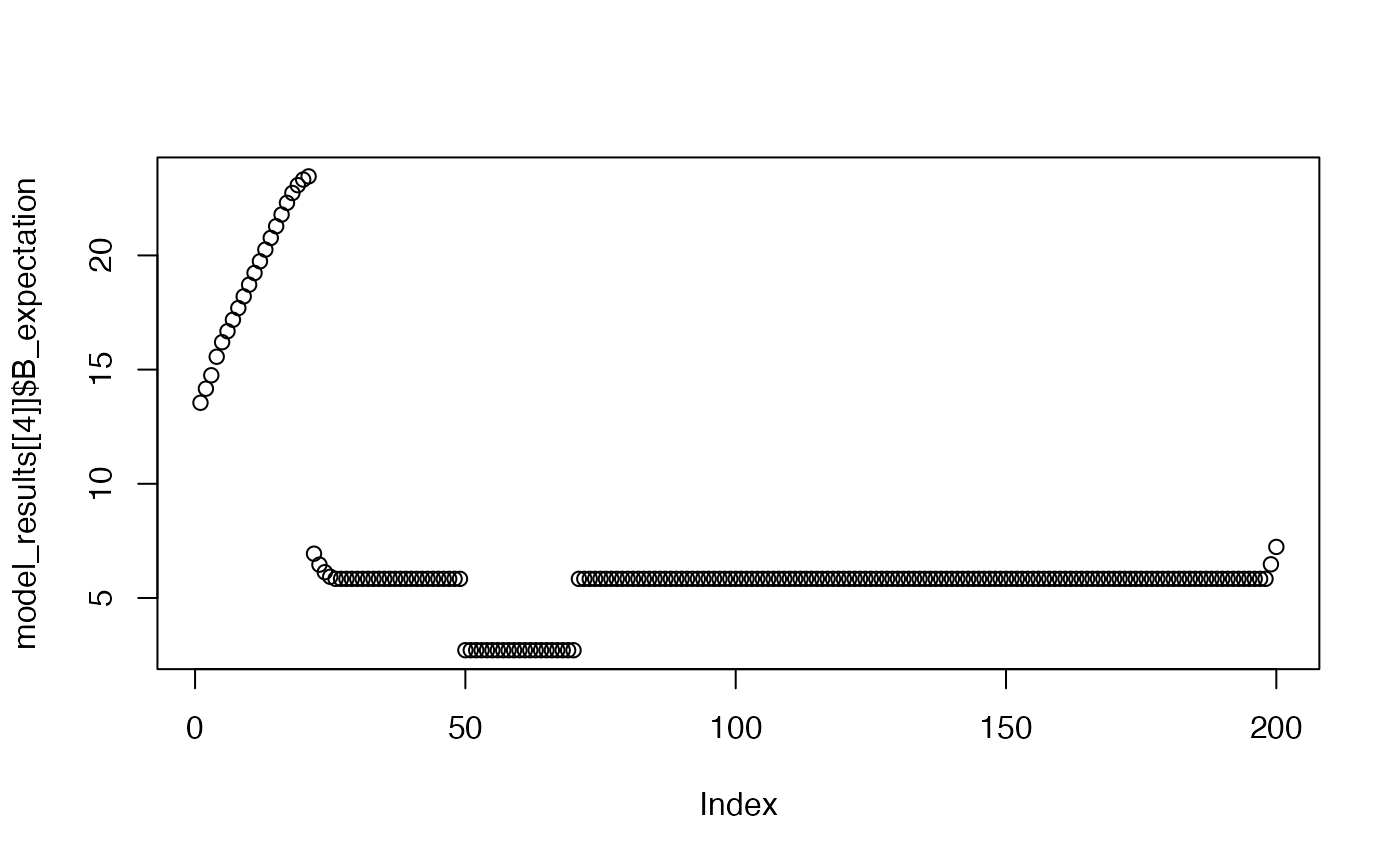
plot(model_results[[4]]$C_expectation)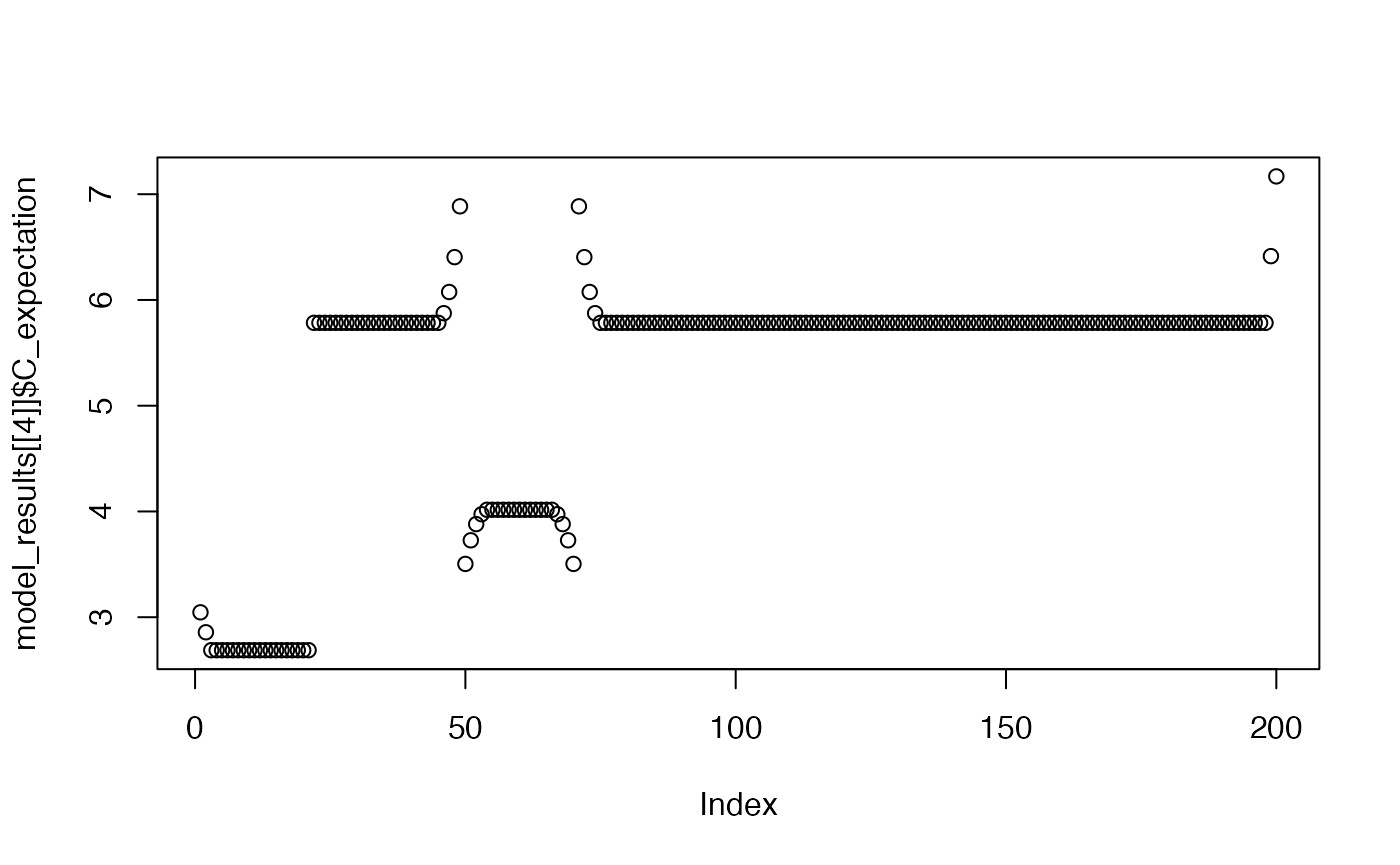
plot(model_results[[4]]$D_expectation)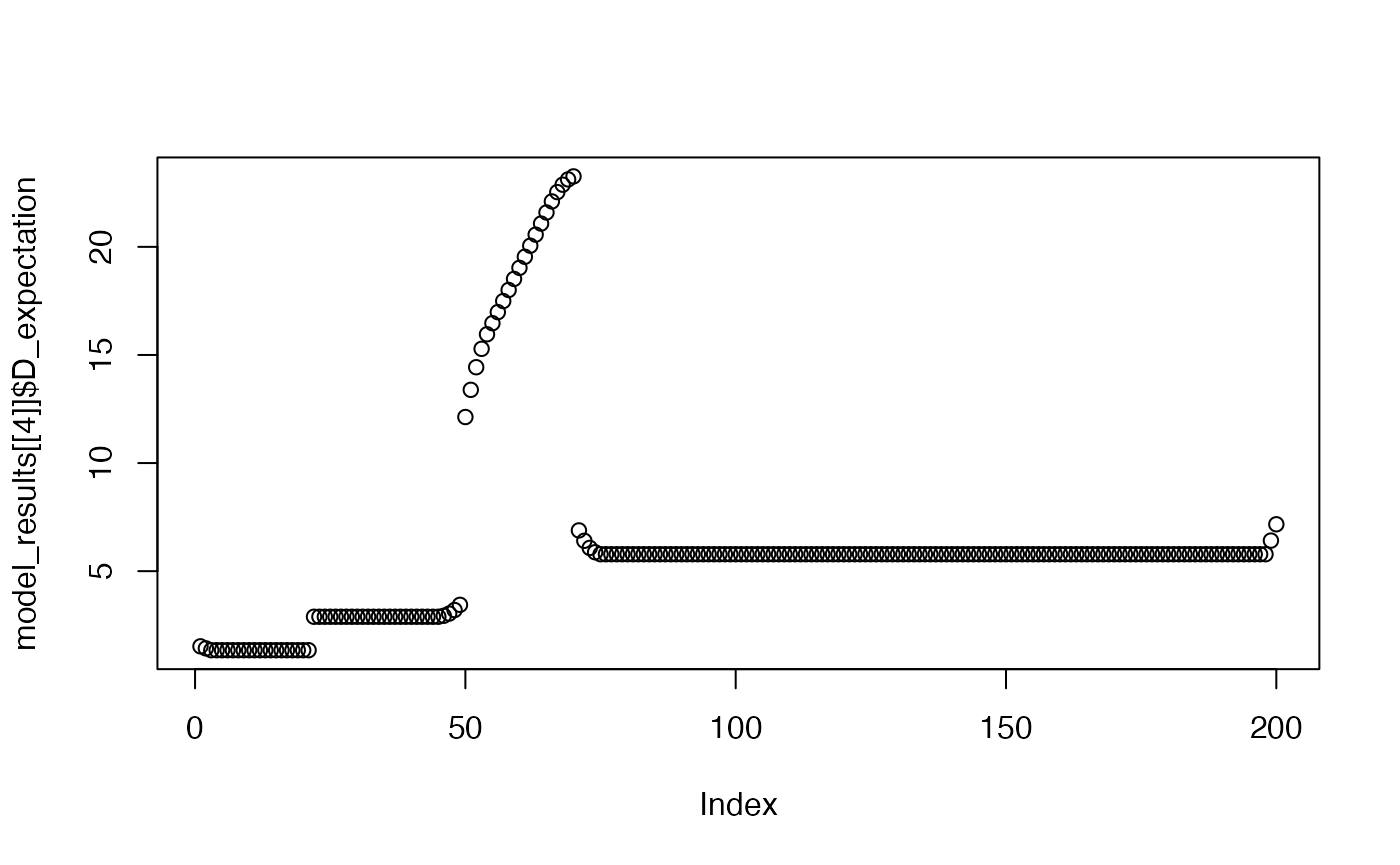
plot(model_results[[9]]$A_expectation)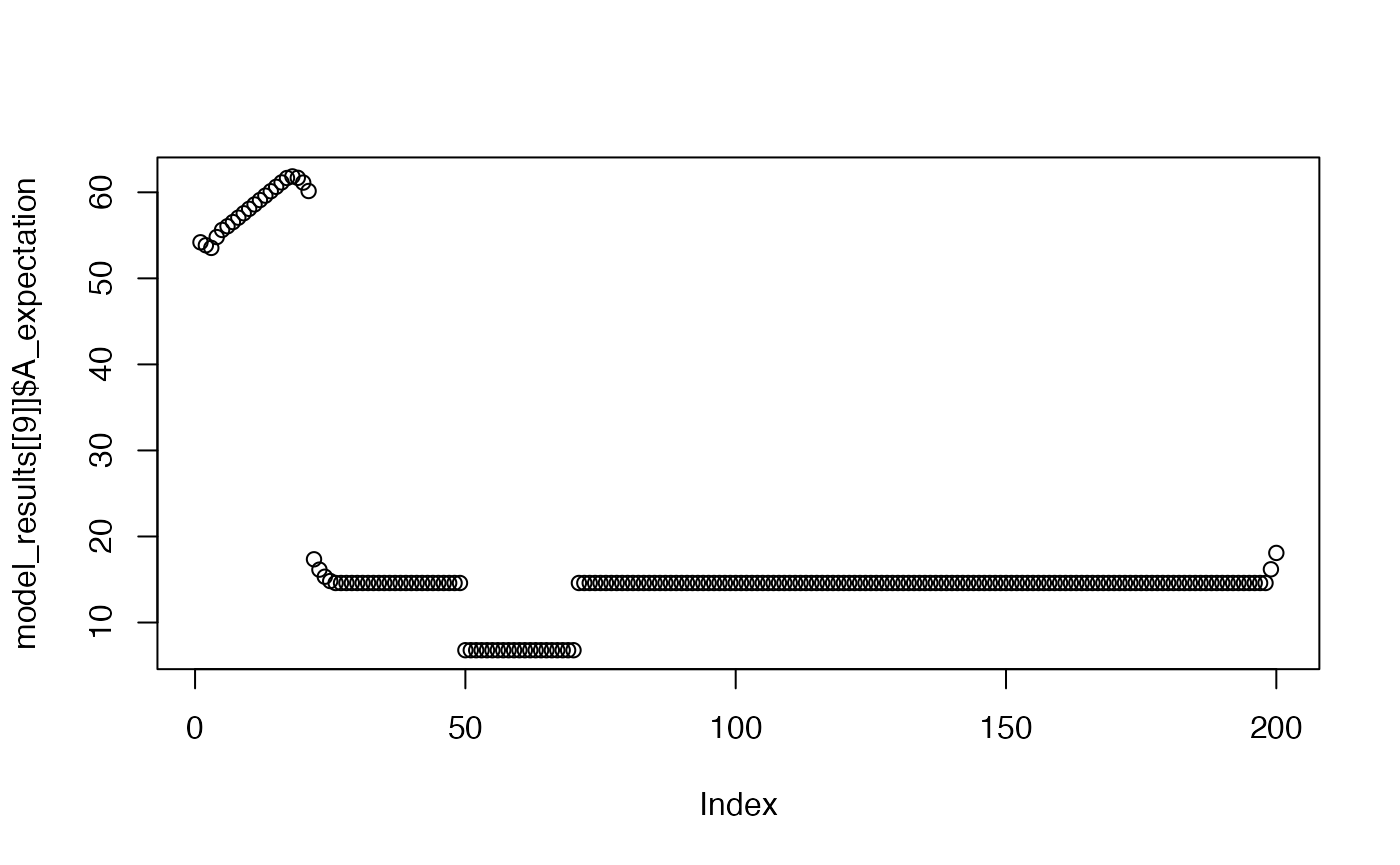
plot(model_results[[9]]$B_expectation)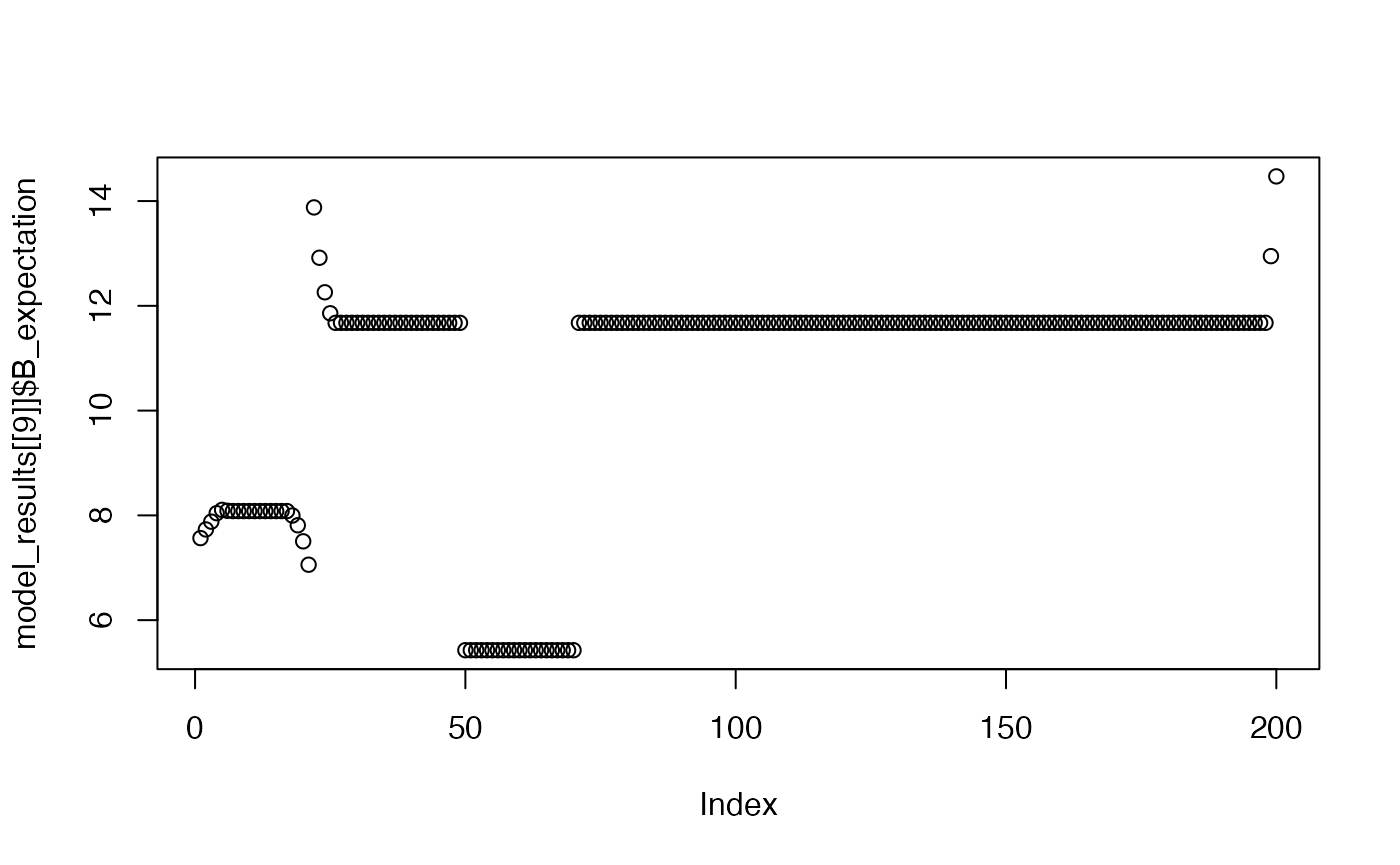
plot(model_results[[9]]$C_expectation)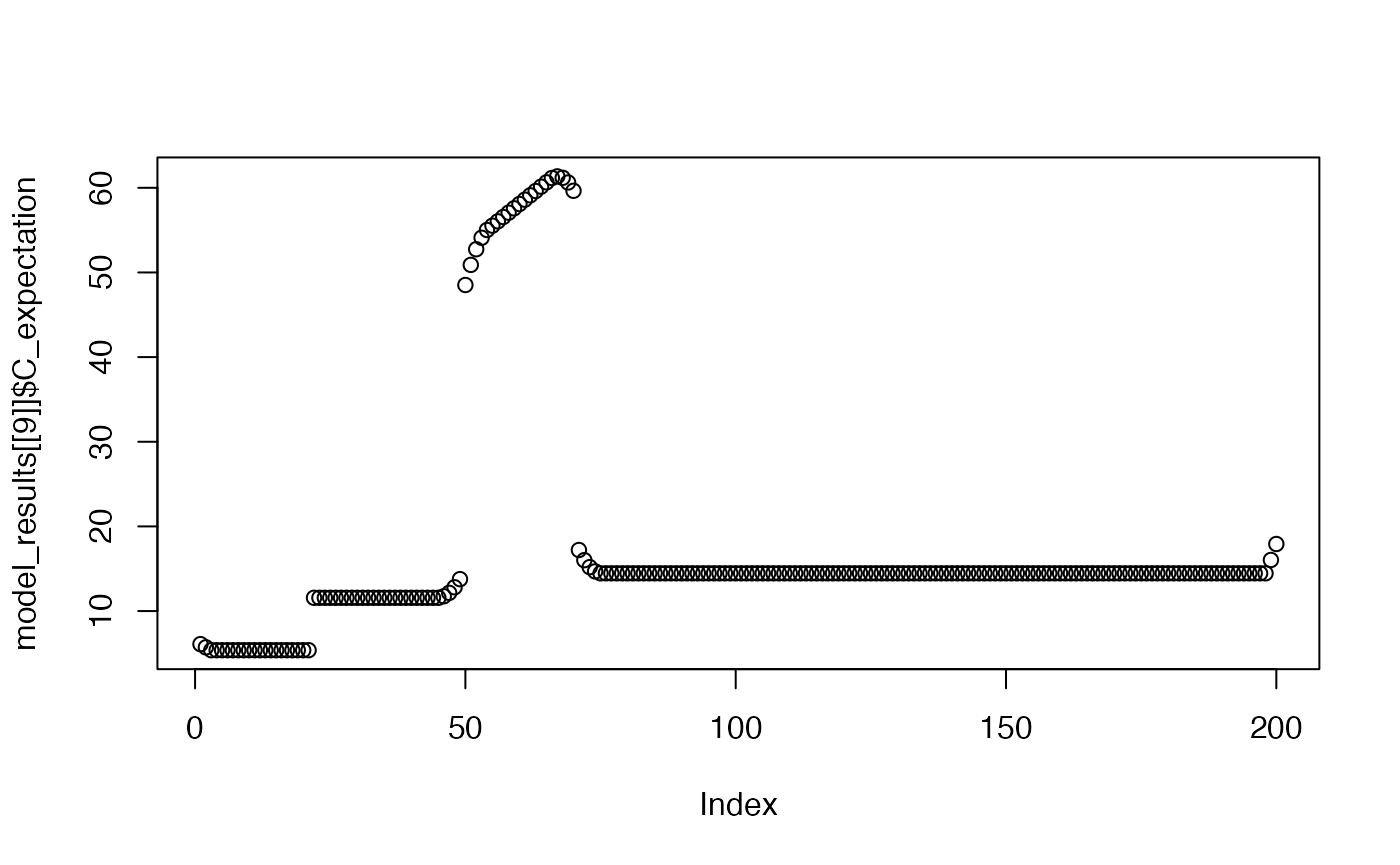
plot(model_results[[9]]$D_expectation)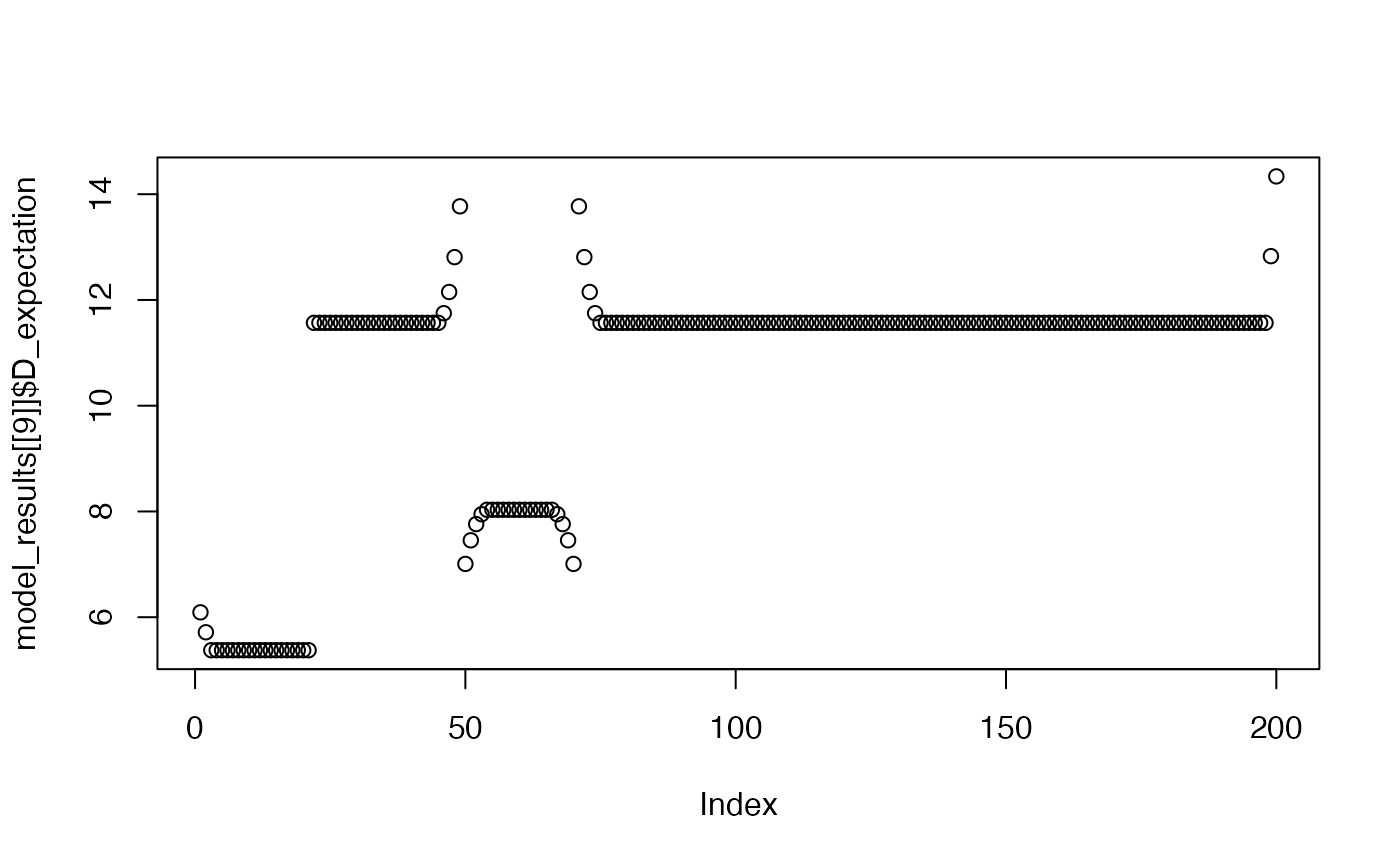
plot(model_results[[10]]$A_expectation)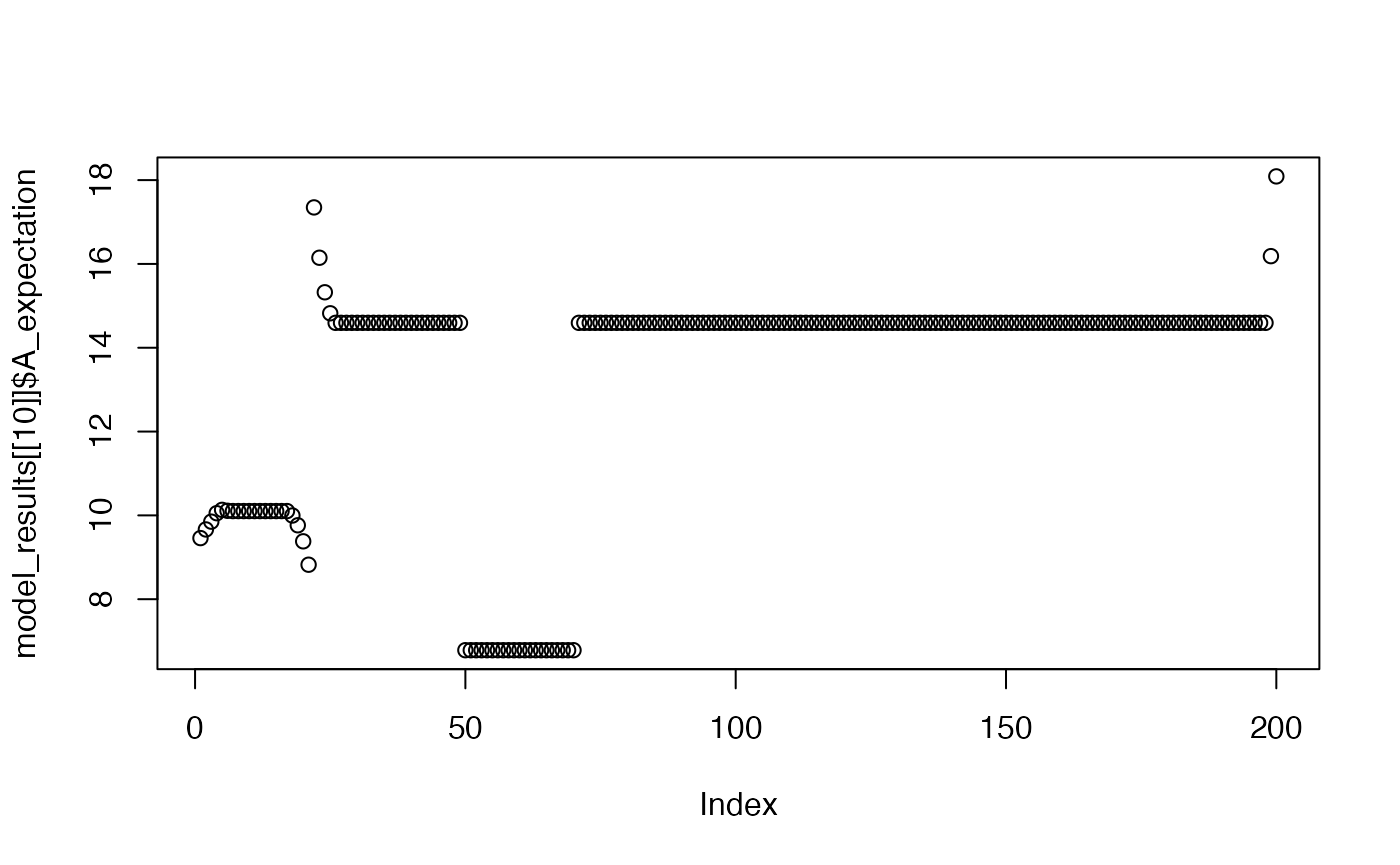
plot(model_results[[10]]$B_expectation)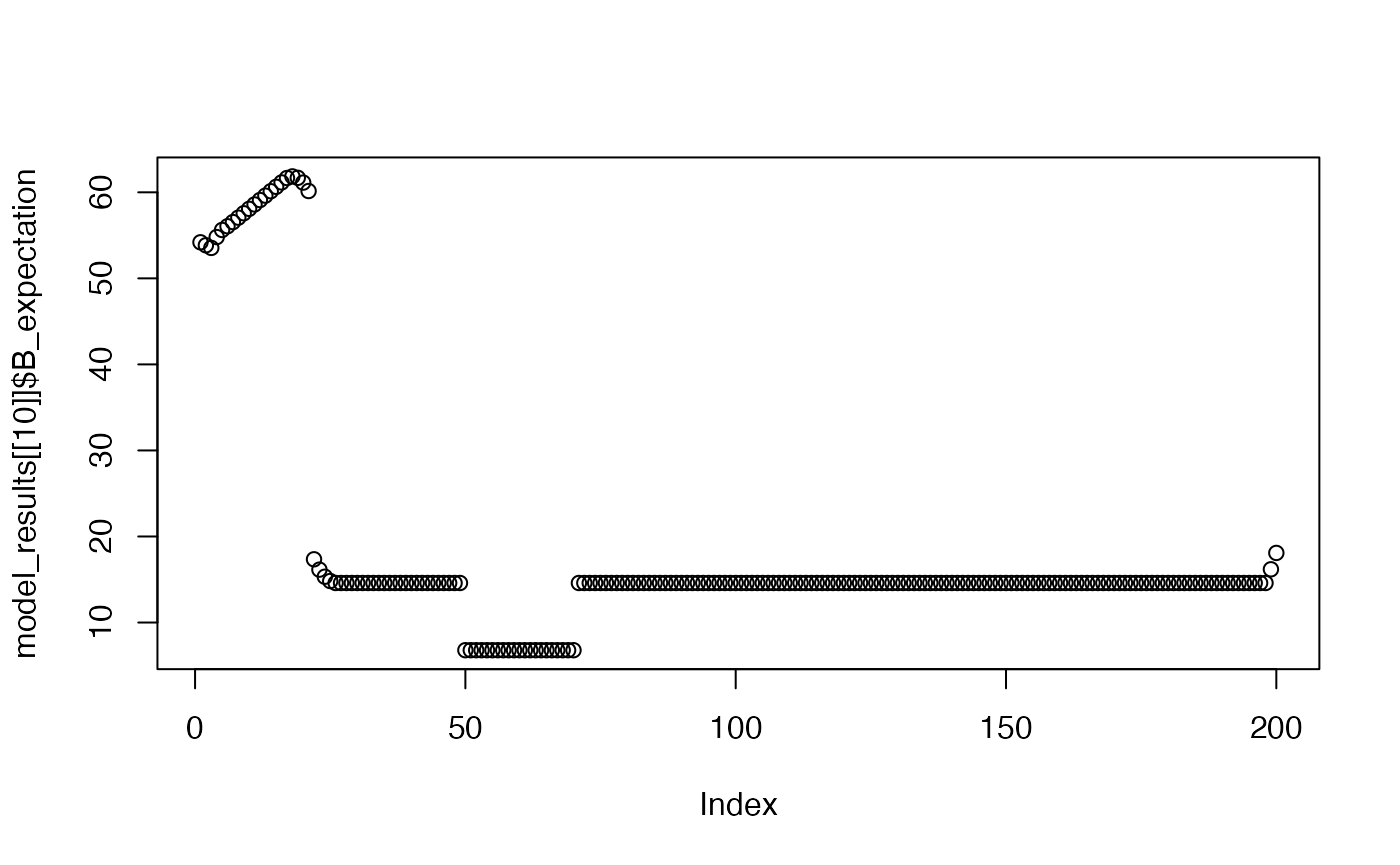
plot(model_results[[10]]$C_expectation)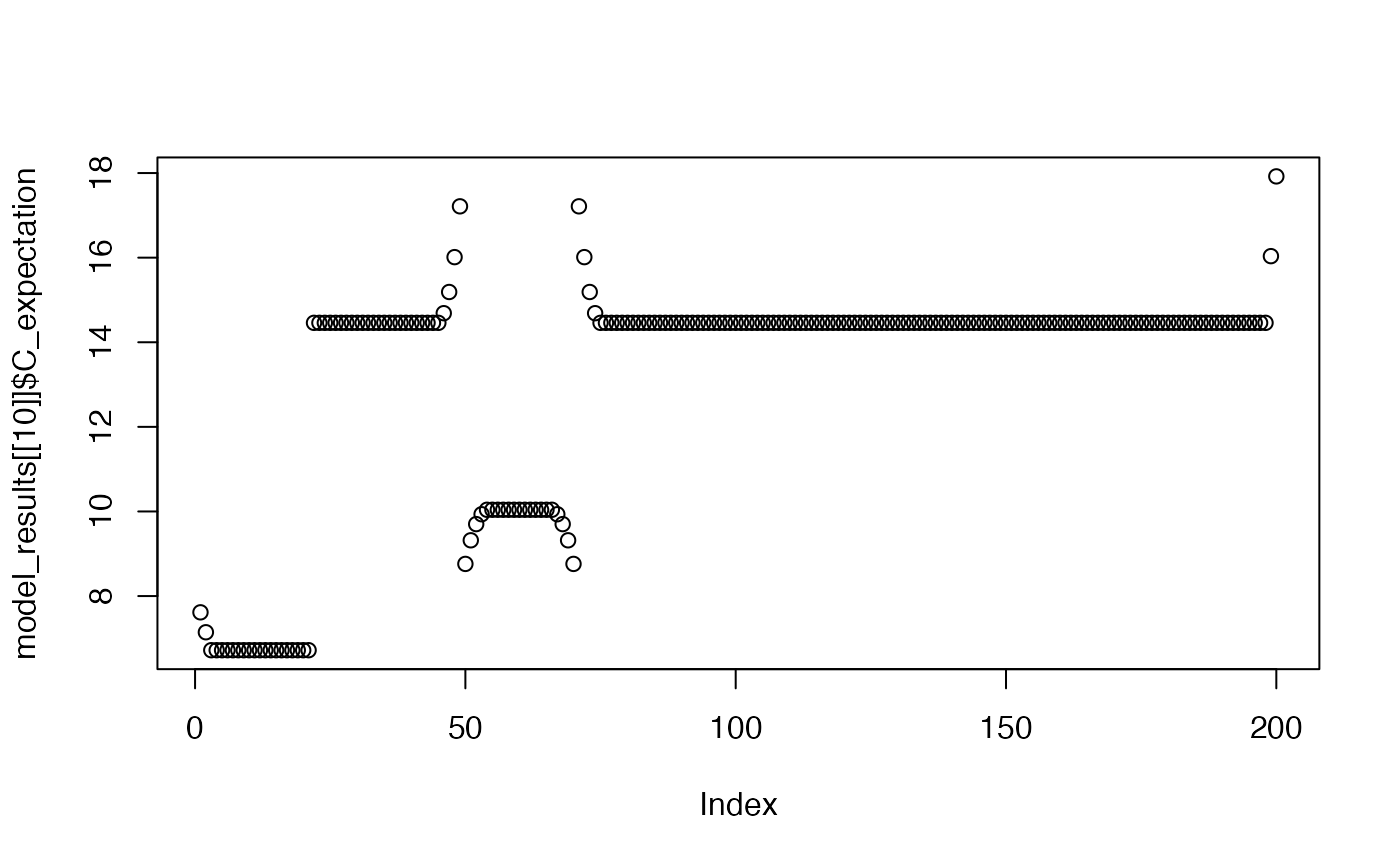
plot(model_results[[10]]$D_expectation)