library(dplyr)
library(tidyverse)
library(jsonlite)
library(xtable)
library(data.table)E1_Power_Analysis
Plan for power analysis.
- Use data from E1B to estimate average proportion recalled per cell in the design.
- Use the proportion as probability for a binomial distribution.
- Simulate recall data in the design
- Estimate number of subjects needed for different effect sizes
Load libraries
Import Data
# Read the text file from JATOS ...
read_file('data/E1B_self_reference_deID.JSON') %>%
# ... split it into lines ...
str_split('\n') %>% first() %>%
# ... filter empty rows ...
discard(function(x) x == '') %>%
# ... parse JSON into a data.frame
map_dfr(fromJSON, flatten=T) -> all_dataDemographics
library(tidyr)
demographics <- all_data %>%
filter(trial_type == "survey-html-form") %>%
select(ID,response) %>%
unnest_wider(response) %>%
mutate(age = as.numeric(age))
age_demographics <- demographics %>%
summarize(mean_age = mean(age),
sd_age = sd(age),
min_age = min(age),
max_age = max(age))
factor_demographics <- apply(demographics[-1], 2, table)Pre-processing
Case judgment accuracy
Get case judgment accuracy for all participants.
case_judgment <- all_data %>%
filter(encoding_trial_type == "study_word",
study_instruction == "case") %>%
mutate(response = as.character(unlist(response))) %>%
mutate(accuracy = case_when(
response == "0" & letter_case == "upper" ~ 1,
response == "1" & letter_case == "upper" ~ 0,
response == "0" & letter_case == "lower" ~ 0,
response == "1" & letter_case == "lower" ~ 1
)) %>%
group_by(ID) %>%
summarise(percent_correct = mean(accuracy))
ggplot(case_judgment, aes(x=percent_correct))+
geom_histogram() +
geom_vline(xintercept=.7)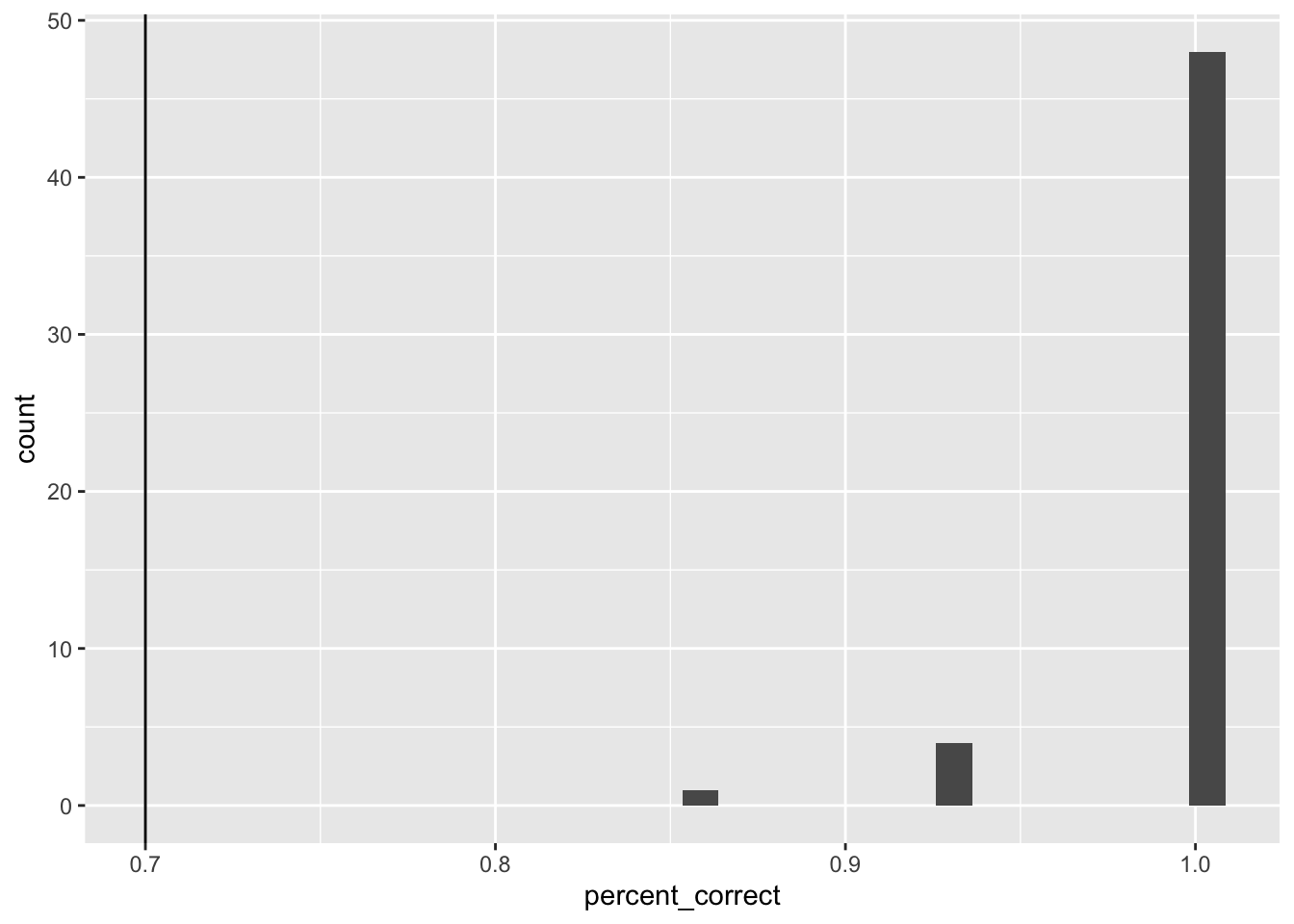
All exclusions
no exclusions
all_excluded <- case_judgment %>%
filter(percent_correct < .7) %>%
select(ID) %>%
pull()
length(all_excluded)[1] 0filtered_data <- all_data %>%
filter(ID %in% all_excluded == FALSE) Accuracy analysis
Define Helper functions
To do, consider moving the functions into the R package for this project
# attempt general solution
## Declare helper functions
################
# get_mean_sem
# data = a data frame
# grouping_vars = a character vector of factors for analysis contained in data
# dv = a string indicated the dependent variable colunmn name in data
# returns data frame with grouping variables, and mean_{dv}, sem_{dv}
# note: dv in mean_{dv} and sem_{dv} is renamed to the string in dv
get_mean_sem <- function(data, grouping_vars, dv, digits=3){
a <- data %>%
group_by_at(grouping_vars) %>%
summarize("mean_{ dv }" := round(mean(.data[[dv]]), digits),
"sem_{ dv }" := round(sd(.data[[dv]])/sqrt(length(.data[[dv]])),digits),
.groups="drop")
return(a)
}
################
# get_effect_names
# grouping_vars = a character vector of factors for analysis
# returns a named list
# list contains all main effects and interaction terms
# useful for iterating the computation means across design effects and interactions
get_effect_names <- function(grouping_vars){
effect_names <- grouping_vars
if( length(grouping_vars > 1) ){
for( i in 2:length(grouping_vars) ){
effect_names <- c(effect_names,apply(combn(grouping_vars,i),2,paste0,collapse=":"))
}
}
effects <- strsplit(effect_names, split=":")
names(effects) <- effect_names
return(effects)
}
################
# print_list_of_tables
# table_list = a list of named tables
# each table is printed
# names are header level 3
print_list_of_tables <- function(table_list){
for(i in 1:length(table_list)){
cat("###",names(table_list[i]))
cat("\n")
print(knitr::kable(table_list[[i]]))
cat("\n")
}
}Conduct Analysis
Recall Test Data
# obtain recall data from typed answers
recall_data <- filtered_data %>%
filter(phase %in% c("recall_1","recall_2") == TRUE ) %>%
select(ID,phase,paragraph) %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = phase,
values_from = paragraph) %>%
mutate(recall_1 = paste(recall_1,recall_2,sep = " ")) %>%
select(ID,recall_1) %>%
# separate_longer_delim(cols = recall_1,
# delim = " ") %>%
mutate(recall_1 = tolower(recall_1)) %>%
mutate(recall_1 = gsub("[^[:alnum:][:space:]]","",recall_1))
encoding_words_per_subject <- filtered_data %>%
filter(encoding_trial_type == "study_word",
phase == "main_study")
recall_data <- left_join(encoding_words_per_subject,recall_data,by = 'ID') %>%
mutate(recall_1 = strsplit(recall_1," "))
# implement a spell-checking method
recall_success <- c()
min_string_distance <- c()
for(i in 1:dim(recall_data)[1]){
recalled_words <- unlist(recall_data$recall_1[i])
recalled_words <- recalled_words[recalled_words != ""]
if (length(recalled_words) == 0 ) recalled_words <- "nonerecalled"
recall_success[i] <- tolower(recall_data$target_word[i]) %in% recalled_words
min_string_distance[i] <- min(sapply(recalled_words,FUN = function(x) {
stringdist::stringdist(a=x,b = tolower(recall_data$target_word[i]), method = "lv")
}))
}
# recall proportion correct by subject
recall_data_subject <- recall_data %>%
mutate(recall_success = recall_success,
min_string_distance = min_string_distance) %>%
mutate(close_recall = min_string_distance <= 2) %>%
group_by(ID,study_instruction,encoding_recall,block_type) %>%
summarise(number_recalled = sum(recall_success),
number_close_recalled = sum(close_recall)) %>%
ungroup() %>%
mutate(proportion_recalled = case_when(encoding_recall == "no_recall" ~ number_close_recalled/6,
encoding_recall == "recall" ~ number_close_recalled/6)) %>%
mutate(ID = as.factor(ID),
study_instruction = as.factor(study_instruction),
encoding_recall = as.factor(encoding_recall),
block_type = as.factor(block_type))
# power analysis parameters from empirical data
mean_p_recall_per_cell <- mean(recall_data_subject$proportion_recalled)
sd_p_recall_per_cell <- sd(recall_data_subject$proportion_recalled)
emp_dist_p_recall_per_cell <- recall_data_subject$proportion_recalledPower-analysis
Very simple approach. Use the mean_p_recall_per_cell to generate data from a binomial distribution.
6 observations per cell (comparison between cells, simple effects)
# This number came from empirical data
mean_p_recall_per_cell <- .2
# create a tibble to store simulation results
sim_data <- tibble()
# simulation parameters
num_sims <- 200 # number of times to a run a simulated experiment
number_of_subs <- c(10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,150,200)
effect_sizes <- c(.01,.02,.03,.04,.05,.1,.2)
# Loop to run all simulations for every parameter
for(n in number_of_subs) {
print(n) # shows simulation progress in the console
for (effect in effect_sizes) {
p_vals <-
rep(0, num_sims) # initialize variable to store p values from each experiment
# run simulated experiments
for (reps in 1:num_sims) {
# A uses rbinom to simulated how many words a person remembers given the base probability
A <-
colMeans(replicate(n, rbinom(6, 1, mean_p_recall_per_cell)))
# B adds the effect size to the base probability
B <-
colMeans(replicate(n, rbinom(
6, 1, mean_p_recall_per_cell + effect
)))
# run a t-test to compare whether the two are different
t_test <- t.test(A, B, paired = TRUE)
# store the p-value in the vector
p_vals[reps] <- t_test$p.value
}
# add the results to a tibble with one row
sim_result <- tibble(
subs = n,
effect_size = effect,
rep = reps,
prop_p_value = length(p_vals[p_vals < .05]) / num_sims # this is proportion of significant experiments, or power
)
sim_data <- rbind(sim_data, sim_result)
}
}[1] 10
[1] 20
[1] 30
[1] 40
[1] 50
[1] 60
[1] 70
[1] 80
[1] 90
[1] 100
[1] 150
[1] 200# summarize the data for plotting
sim_data_means <- sim_data %>%
mutate(effect_size = as.factor(effect_size)) %>%
group_by(subs,effect_size) %>%
summarise(mean_proportion = mean(prop_p_value), .groups = 'drop')
# plot the data
ggplot(sim_data_means,
aes(x=subs,
y=mean_proportion,
group = effect_size,
color = effect_size)) +
geom_point()+
geom_line()+
ylab("Proportion of significant experiments (Power)")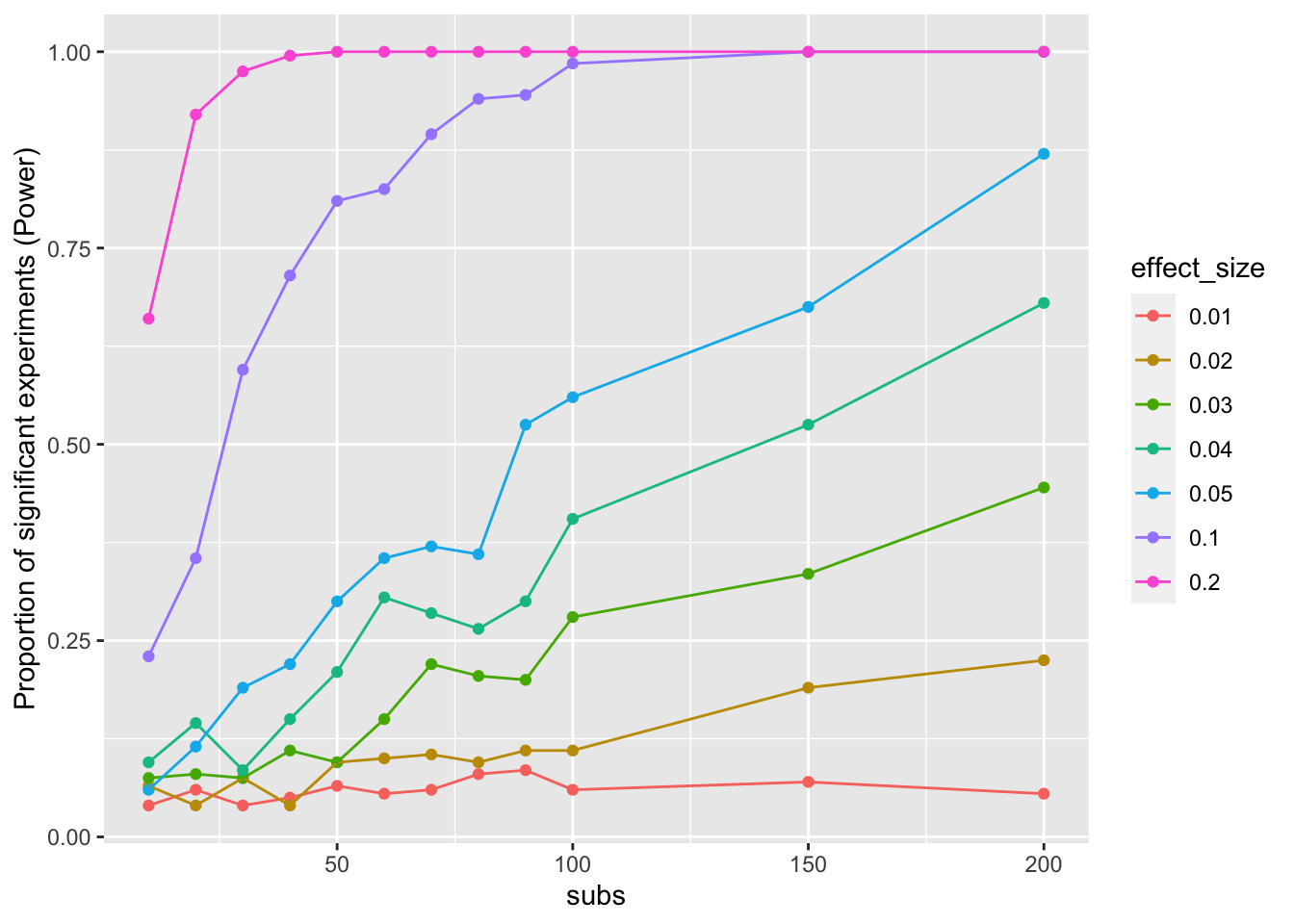
12 observations per cell: simple effects for main effect of levels of processing
sim_data <- tibble()
num_sims <- 200
number_of_subs <- c(10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90,100,150,200)
effect_sizes <- c(.01,.02,.03,.04,.05,.1,.2)
for(n in number_of_subs){
print(n)
for(effect in effect_sizes){
p_vals <- rep(0,num_sims)
for(reps in 1:num_sims){
A <- colMeans(replicate(n, rbinom(12,1,mean_p_recall_per_cell)))
B <- colMeans(replicate(n, rbinom(12,1,mean_p_recall_per_cell+effect)))
t_test <- t.test(A,B,paired = TRUE)
p_vals[reps] <- t_test$p.value
}
sim_result <- tibble(subs = n,
effect_size = effect,
rep = reps,
prop_p_value = length(p_vals[p_vals < .05])/num_sims)
sim_data <- rbind(sim_data,sim_result)
}
}[1] 10
[1] 20
[1] 30
[1] 40
[1] 50
[1] 60
[1] 70
[1] 80
[1] 90
[1] 100
[1] 150
[1] 200sim_data_means <- sim_data %>%
mutate(effect_size = as.factor(effect_size)) %>%
group_by(subs,effect_size) %>%
summarise(mean_proportion = mean(prop_p_value), .groups = 'drop')
ggplot(sim_data_means,
aes(x=subs,
y=mean_proportion,
group = effect_size,
color = effect_size)) +
geom_point()+
geom_line()
save data
save.image("data/E1_Power.RData")